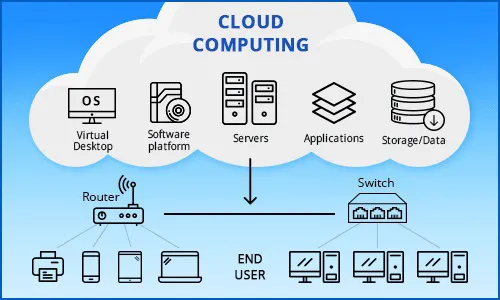
In today’s digital age, cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals manage, store, and process data. This transformative technology has enabled unprecedented scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of cloud computing software, exploring its definition, types, benefits, and key players in the market.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of various services over the internet, including storage, processing power, and applications. It allows users to access and utilize computing resources on-demand, eliminating the need for physical hardware and reducing the burden of managing complex IT infrastructure.
Cloud computing can be broadly categorized into three primary service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This model provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks on a pay-as-you-go basis. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform and environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This model includes services such as databases, middleware, and development tools. Examples of PaaS providers are Heroku, Google App Engine, and Red Hat OpenShift.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications through a web browser, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance. Notable SaaS providers include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Adobe Creative Cloud.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing Software
Cloud computing software offers a multitude of benefits, making it a compelling choice for businesses of all sizes. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for significant capital investments in hardware and infrastructure. Instead, users pay for the resources they use, resulting in substantial cost savings. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go model allows for better budget predictability and financial flexibility.
- Scalability: Cloud services can easily scale up or down based on demand. This flexibility ensures that businesses can handle varying workloads without overprovisioning or underutilizing resources. Whether it’s a sudden traffic spike or seasonal fluctuations, cloud computing can adapt to meet the needs.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Cloud computing enables access to data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility fosters collaboration among teams, regardless of their geographical location. Employees can work remotely, share files in real-time, and collaborate on projects seamlessly.
- Disaster Recovery and Data Backup: Cloud providers offer robust disaster recovery and backup solutions. Data stored in the cloud is often replicated across multiple data centers, ensuring high availability and resilience. In the event of a hardware failure or data loss, businesses can quickly restore their operations with minimal downtime.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Cloud computing software providers handle updates, patches, and maintenance tasks, relieving users of the burden of managing software and infrastructure. This ensures that applications are always up-to-date and secure, without requiring manual intervention.
- Enhanced Security: Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications. These security features help protect sensitive data and ensure that businesses meet regulatory requirements.
Types of Cloud Computing Software
Cloud computing software encompasses a wide range of tools and services designed to meet diverse business needs. Let’s explore some of the most common types of cloud computing software:
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage services provide a scalable and cost-effective solution for storing and managing data. Users can upload, store, and retrieve files from the cloud, eliminating the need for physical storage devices. Examples include Amazon S3, Google Drive, and Dropbox.
- Cloud Databases: Cloud databases offer a managed database service, allowing users to store, retrieve, and manage data without the need for on-premises database servers. These databases are highly scalable and provide automated backups and replication. Popular cloud databases include Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, and Microsoft Azure SQL Database.
- Cloud Collaboration Tools: Cloud collaboration tools facilitate communication and teamwork among employees. These tools often include features such as file sharing, real-time editing, and project management. Examples are Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Google Workspace.
- Cloud Backup and Recovery: Cloud backup services provide a secure and reliable solution for backing up data to the cloud. In the event of data loss or disaster, users can quickly restore their data from the cloud backup. Notable cloud backup providers include Backblaze, Carbonite, and Acronis.
- Cloud Development and Testing: Cloud-based development and testing platforms enable developers to build, test, and deploy applications in a cloud environment. These platforms offer a range of development tools, pre-configured environments, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Examples include AWS Cloud9, GitHub Codespaces, and Azure DevOps.
- Cloud AI and Machine Learning: Cloud AI and machine learning services provide powerful tools and frameworks for developing and deploying artificial intelligence applications. These services include pre-trained models, data processing pipelines, and scalable infrastructure for training and inference. Leading providers in this space are Google AI Platform, AWS SageMaker, and IBM Watson.
- Cloud Networking: Cloud networking services enable businesses to create and manage virtual networks, load balancers, and VPNs in the cloud. These services ensure secure and efficient communication between cloud resources and on-premises systems. Prominent cloud networking solutions include AWS VPC, Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud, and Azure Virtual Network.
Key Players in the Cloud Computing Market
The cloud computing market is dominated by several key players, each offering a comprehensive suite of services. Here are some of the leading cloud computing providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is the market leader in cloud computing, offering a vast array of services ranging from computing power and storage to machine learning and analytics. With its global presence and extensive ecosystem, AWS is the go-to choice for many businesses.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure is a close competitor to AWS, providing a wide range of cloud services and integrations with Microsoft’s software products. Azure is known for its strong hybrid cloud capabilities, enabling seamless integration with on-premises environments.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP offers a robust set of cloud services, with a focus on data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. Google’s expertise in data processing and analytics makes GCP a preferred choice for data-intensive applications.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud provides a range of cloud services, with a strong emphasis on enterprise solutions and hybrid cloud deployments. IBM’s expertise in AI, blockchain, and security makes it a compelling option for large enterprises.
- Oracle Cloud: Oracle Cloud is known for its database services and enterprise applications. Oracle’s cloud offerings are designed to support mission-critical workloads and provide seamless integration with Oracle’s software products.
- Alibaba Cloud: Alibaba Cloud is a major player in the Asia-Pacific region, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud services. With its strong presence in China and expanding global footprint, Alibaba Cloud is a significant competitor in the cloud market.
The Future of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing looks incredibly promising, with several key trends shaping its evolution:
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computing resources closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving performance. This trend is particularly relevant for applications requiring real-time processing, such as IoT devices and autonomous vehicles.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: Businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in and leverage the best features of different cloud providers. This approach enables greater flexibility and resilience.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing allows developers to build and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. This trend is gaining traction due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and scalability.
- AI and Machine Learning: Cloud providers are investing heavily in AI and machine learning services, making advanced analytics and automation accessible to businesses of all sizes. This trend will continue to drive innovation and efficiency.
- Security and Compliance: As cloud adoption grows, so does the focus on security and compliance. Cloud providers will continue to enhance their security measures and offer tools to help businesses meet regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Cloud computing software has transformed the way businesses operate, offering unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. From storage and databases to collaboration tools and AI services, the cloud provides a wide range of solutions to meet diverse needs. As technology continues to evolve, the future of cloud computing holds exciting possibilities, promising even greater innovation and impact on our digital lives. Embracing cloud computing is no longer a choice but a necessity for businesses looking to stay competitive and thrive in the digital era.